Arraid manufacturers solid state Flashtape and Flashdisk solutions for computer systems by Bull, DEC, Encore, Honeywell, HP, Evans and Sutherland, Pertec, SMD, HISI, HPIB, MAC, OMTI, XMD and many more.
Using proprietary FPGA based technology, Arraid are able to replace aging and refurbished drives offering reliable and supportable solid state disk and solid state tape drives with on-board network capability.
Arraid offer Network Attached Storage solutions when the Arraid TES & AEM product solutions are configured and installed with the Arraid Flash Drive (AFD with Network feature enabled).
The Network enabled AFD is also available as a solid state, drop-in replacement for SCSI and Floppy connector drives.
Note the Optional Network /ethernet feature support is offered for centralised backup & restore capability removing the need to rotate media. Primary data storage is always written to the CF card.
The AFD is also available without Network enabled firmware.

The Network enabled Arraid SCSIFlash Drive (ASFD) replaces SCSI hard drives SCSI SSD drives, SCSI Magneto Optic, SCSI Floppy, SCSI PC Cards, SCSI PCMCIA cards, SCSI Zip drives.
The SCSIFlash Network/ Ethernet drive (ASFD-E) is currently available in two physical form factors;
- SCSI Hard Disk Drive (HDD) and SCSI SSD replacement with no external removable storage device
- SCSI Magneto-Optical (MO) SCSI Tape, SCSI PC Cards, SCSI PCMCIA cards, SCSI Zip and SCSI Floppy drive replacements with externally removable CF memory card slot
The network enabled Arraid FLOPPYFlash Drive (AFFD) currently supports four physical connector interfaces with full height and half height frames options;
- SLIM-26
- FLAT-34
- 5.25”
- 8 Shugart

Overview
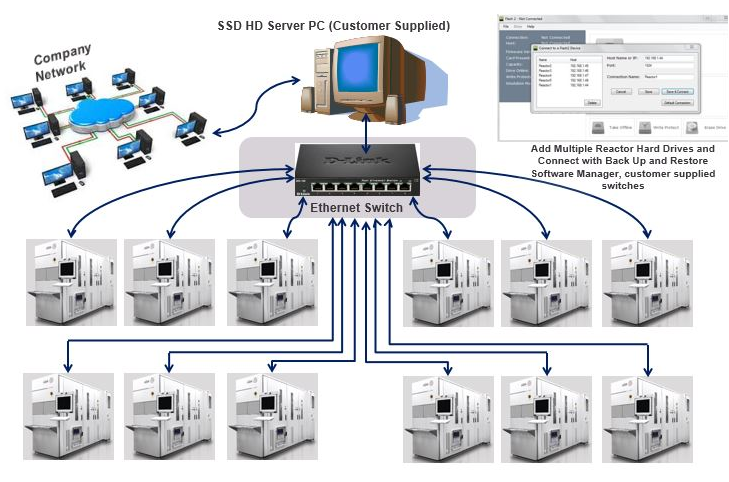
The Arraid Flash Drive (AFD) with Network feature enabled offers vital back-up and restore capability to be made as a complete disk image of its CompactFlash card at any given point in time and transferred via an Ethernet network to be stored remotely from the legacy equipment and restored as and if needed. Universal TCP is used for disk image transfers with remote execution of back-up and restore configuration operations controlled via the on board Windows GUI, or user API /CLI and auto-online implemented on back-up completion.
The Compact Flash (CF) based Flash based Ethernet back-up and restore capability generates considerable savings in time and expense in the face of process outages. In semiconductor manufacturing, for example, process outages can cost in excess of $1,000/$100,000 per hour/day. In the telecommunications industry they may incur considerable fines.
The Arraid Flash Drive (AFD) with Network back-up and restore capability can also be used to replace traditional manual rotation of media with remote download of manufacturing files so that, for example, a CNC machine knows what program to run for a particular session or a semiconductor fab which recipe to use.
The AFD is a completely programmable replacement solution, enabling the legacy device implementation nuances of all equipment manufacturers to be fully emulated.
The ASFD (SCSI) Flash combines proven SCSI drive architectures (SASI, SCSI-1, SCSI-2) with industry-standard, solid state CompactFlash card technology to provide a high-reliability, solid state replacement for any style of SCSI-based drive including hard disk, magneto optical, tape and floppy drives.
The Compact Flash based Solid State Network emulation drive offers Ethernet back-up and restore capability offering the added benefit of being able take snapshots of the data and keep it offline from the legacy equipment with the option to restore at a later date, if necessary.
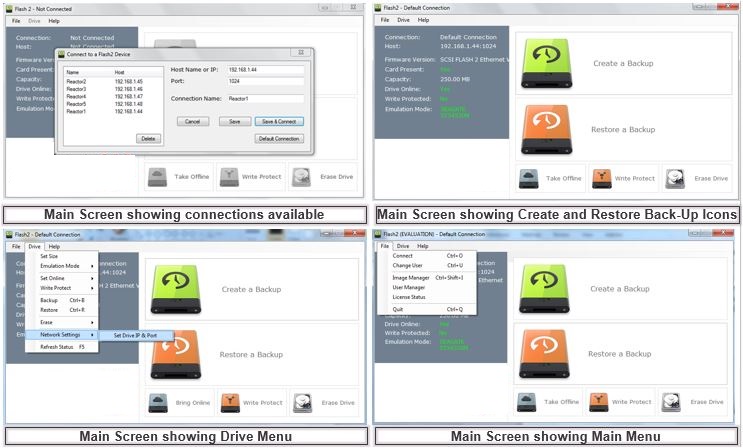
Demonstrations of how to use FLASHGUI on SCSIFlash™ and FLOPPYFlash™ for configuration and control, back-up and restore and the selection of different drive emulations, can be seen of Solid State Disk’s YouTube channel:
Chapter 1 “How to Video Collection” - Flash2GUI Network Software.
Part 1 – Installing Flash2GUI Software.
Part 2 – Connecting Flash2GUI to the Solid State Drive
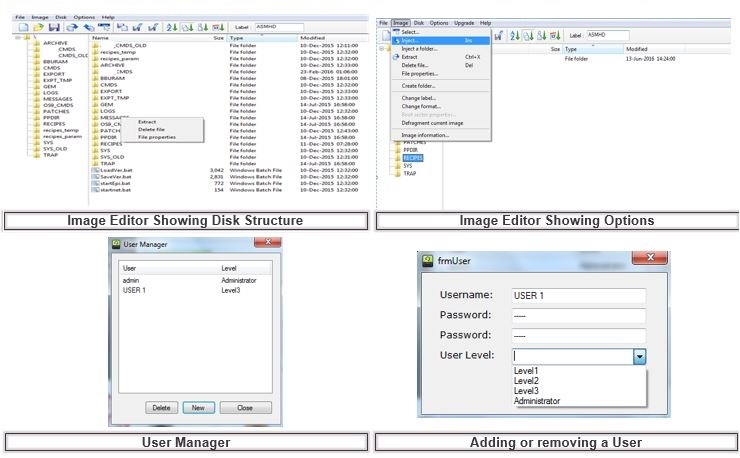
Part 3 – Navigating the Flash2GUI File Menu Highlights – New IP Connections & Names, Change User, User Manager & User Permissions & License Status
Part 4 – Performing Backup and Restore Functions
Part 5 – Navigating the Drive Menu ( part 1 of 2) Highlights – Drive Size, Capacity Settings, Emulation Change, Online / Offline Status, Write Protect, Erase
Part 5(2) – Navigating the Drive Menu ( part 2 of 2) Highlights – Network Settings ( IP & Port), Subnet Mask, Get SCSI Trace File Function, Executing Commands & Scripts
Part 6 – Navigating the Help Menu Highlights – Message Logging & Trouble Shooting